From the Concept of "Inflammaging" to P4 Medicine
Human aging is characterized by a chronic low grade on inflammation and this phenomenon has been called “inflammaging."
Inflammaging is a significant risk factor for mortality in elderly people.
Aging phenotypes:
- Change in Body Composition (Less Muscle Mass)
- Less Efficient Energy Production & Utilization
- Loss of Metabolic Homeostasis
- Decrease in Acquired Immunity
- Increase in Low-Grade Systemic Inflammation
- Hormonal Decline
Factors that prevented healthy aging:
- Being Unmarried
- Frailty—Low Body Mass Index
- Low Respiratory Function
- High Diastolic Blood Pressure (>90 mm Hg)
- Past or Current Smoker
- Alcohol Use >15 oz./month
- Elevated Chronic Inflammation
There is evidence that a state of mild and chronic inflammation, revealed by elevated levels of inflammatory biomarkers such as C-reactive protein and IL-6, is associated and predictive of many aging phenotypes, such as:
- Metabolic Homeostasis
- Immune Senescence
- Neuronal Health
- Susceptibility to Infection
IL-6 is the most important cytokine that is shared across age-related pathologies with chronic inflammatory component.
Moreover, inflammatory biomarkers such as IL-6 and TNF alpha down-regulate insulin, insulin-like growth factor 1, erytropietin and protein synthesis after a meal.
Identify biomarkers as IL-6 and TNF alpha could predict ten years ahead all causes of mortality: circulating pro-inflammatory molecules are strong predictors of age related mortality.
Why is the Management of Patients with Chronic Inflammatory Disorders Important?
The study of Dregan et al., 2014 points out that the risk of cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes mellitus is increased across a range of multi-systemic chronic inflammatory disorders (listed in Table 1) with evidence that a risk is associated with severity of inflammation. In the end we can affirm that clinical management of patients with chronic inflammatory disorders should reduce cardiovascular risk as we can see in the table below.
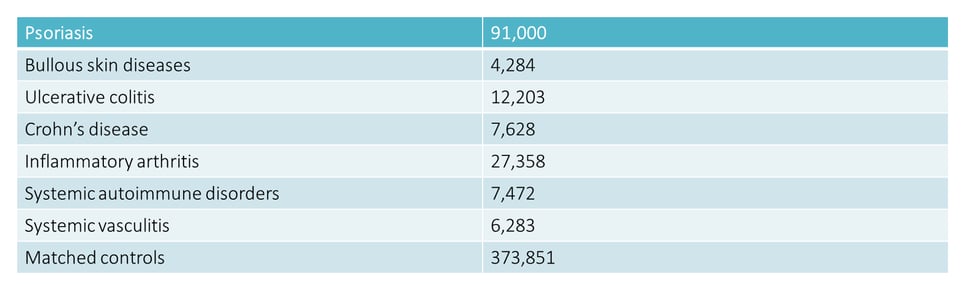 TABLE 1: list of chronic inflammatory disorders and number of people with corresponding pathologies
TABLE 1: list of chronic inflammatory disorders and number of people with corresponding pathologies
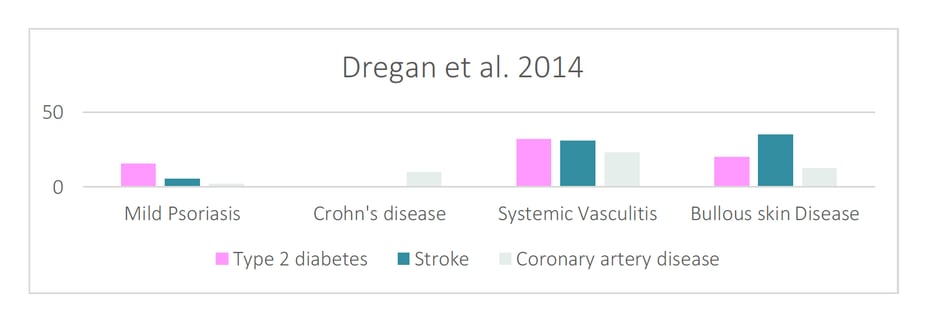
Chronic inflammation may be associated with atheromatous disease, coronary heart disease and stroke, as well as insulin resistance.
Another important article about this phenomenon is on the study of Choi et al that show that there is a stronger association between periodontal disease and diabetes in people having elevated CRP. This may suggest that chronic inflammatory conditions could increase the impact of periodontitis on hyperglycemic status.
Periodontal Health & Prevention of Systemic Chronic Diseases in the Aging Patient
Proportion of adults >65 years of age will grow to 21.7% of the population by 2040 and 98.2 million >65 years of age will be living in US by 2060.
Oral health is an important component of an older adult’s health—in fact, we know that poor oral health can affect systemic health.
The prevalence of periodontitis has been shown to be significantly higher in 70 to 81 years old subjects: periodontitis is the sixth most prevalent chronic condition in the world that can lead to a chronic inflammatory status of the body.
In a recent study in Italy, the prevalence of severe and moderate periodontitis were 34.94% and 40.78%, respectively.
11% of individuals of the global population are affected by the severe type of periodontitis, and it’s more common in older adults. This is why we have to change our way of delivering dental care.
Noncommunicable diseases as cardiovascular disease, cancer, respiratory disease, and type 2 diabetes are now leading causes of death, disability and diminished quality of life in the world. This is because healthcare professionals must evolve into a proactive system.
Now, as healthcare professionals, we have to focus on the prevention of chronic disease and associated risk factors.
The New Approach: P4 Medicine
The new approach focusing on care that is:
- PREDICTIVE: Detecting disease precursors allows pro-active interventions. Predictive medicine is essential for prevention. Clinically useful biomarkers can be use for patient stratification.

- PREVENTIVE: Prevention of chronic disease of the elderly
- PERSONALIZED: Genetic predisposition play a role in inflammaging. Genetic tests lead to the opportunity for patient stratification and improve prevention of chronic diseases
- PARTICIPATORY: Improve health literacy. From the definition of “health literacy” WHO: “People’s knowledge, motivation and competences to access, understand, appraise and apply health information in order to make judgement and take decisions in every day life concerning health care, disease prevention and health promotion to maintain or improve quality of life during the life."
